Forschungsprojekte AG Nagel
Wir beschäftigen uns mit den molekularen Mechanismen, die Stammzellen eine Resilienz gegenüber inneren und äußeren Stressfaktoren verleihen. Schwerpunkte hierbei sind Genomintegrität, Zelldifferenzierung und Wachstumskontrolle, sowie Immunität. Dazu erforschen wir die Funktion des Gens putzig bei der Wachstumskontrolle sowie bei der epigenetischen Regulation der genomischen Stabilität in den Stammzellen der Keimbahn. Zudem ermitteln wir die Funktion spezifischer DNA-Reparaturgene in Drosophila. Desweiteren untersuchen wir den Notch-Signalweg, der zentral ist für die Differenzierung u.a. von Stammzellen z.B. in der Hämatopoese und von Immunzellen. Wir nutzen die neuesten molekularen Techniken in unserer Forschung, u.a. ‚genome engineering‘ mittels Crispr/Cas9. Aufgrund der großen Ähnlichkeit der molekularen Mechanismen zwischen Fliege und Säugern ergeben sich aus dieser Forschung ggfs. neuartige Therapieansätze z.B. bei Leukämien.
Das Gen putzig ist für die Normalentwicklung der Fliege unabdingbar. Es wird bei der Differenzierung von Zellen, der Wachstumskontrolle und der Überwachung der Genomintegrität gebraucht. Diese vielfältigen Funktionen lassen sich dadurch erklären, dass das Putzig Protein ein integraler Bestandteil diverser Multiproteinkomplexe ist, die die Genaktivität epigenetisch oder transkriptionell regulieren. Zuerst entdeckten wir in unserer AG, dass putzig ein wichtiger Regulator des Notch-Signalwegs ist, welcher eine Vielzahl von Entwicklungsprozessen in Tieren steuert. Momentan liegt der Schwerpunkt unserer Forschung auf der epigenetischen Regulation der genomischen Stabilität in den Stammzellen der Keimbahn.
Dieses Projekt wird von der DFG gefördert (NA 427/6-1).
Einige projektrelevante Publikationen dazu:
Kober, L., Zimmermann, M., Kurz, M., Bayer, M., Nagel, A.C. (2019). Loss of putzig in the germline impedes germ cell development by inducing cell death and new niche like microenvironments. Scientific Reports 9:9108. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-45655-5
Zimmermann, M., Kugler, S., Schulz, A., Nagel, A.C. (2015). Loss of putzig activity results in apoptosis during wing imaginal development in Drosophila. PLoS ONE 10(4):e0124652. doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0124652
Kugler, S.J. and Nagel, A.C. (2010). A novel Pzg-NURF complex regulates Notch target gene activity. Molecular Biology of the Cell 21:3433-3448. doi: https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.e10-03-0212
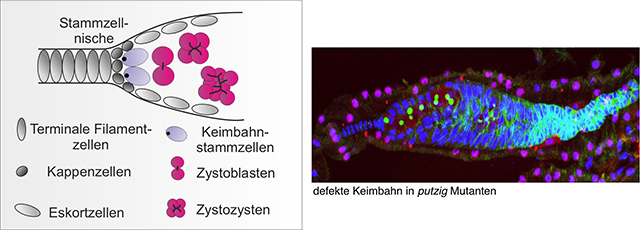
Das Genom unterliegt ständigen äußeren Einflüssen, die seine Integrität bedrohen. Im Laufe der Evolution haben sich vielfältige Reparaturwege herausgebildet, die diesen Schädigungen entgegenwirken. In Modellorganismen wie der Hefe und Drosophila wurden die grundlegenden Mechanismen durch die Analyse beteiligter Gene entschlüsselt. Fehlt diese ständige Reparatur sind schwerwiegende Erkrankungen, insbesondere Krebs und Leukämien, die Folge. In diesem Zusammenhang wurden beim Menschen weitere DNA-Reparaturgene und ihre Funktionen entschlüsselt, die in Drosophila noch nicht untersucht sind. Diese Lücke wollen wir schließen, und nutzen dazu das CRISPR/Cas9 System, um gezielt Mutationen in den noch unerforschten Drosophila-Genen für weitere Untersuchungen zu setzen.
Auszug themennaher Publikationen:
Bayer, F.E., Deichsel, S., Mahl, P., Nagel, A.C. (2020). Drosophila Xrcc2 regulates DNA double-strand repair in somatic cells. DNA Repair (Amst) 88:102807. Link doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dnarep.2020.102807
Bayer, F.E., Zimmermann, M., Preiss, A., Nagel, A.C. (2018). Overexpression of the Drosophila ATR homologous checkpoint kinase Mei-41 induces a G2/M checkpoint in Drosophila imaginal tissue. Hereditas 155:27. Link doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s41065-018-0066-4
Bayer, F.E., Zimmermann, M., Fischer, P., Gromoll, C., Preiss, A., Nagel, A.C. (2017). P53 and Cyclin G cooperate in mediating genome stability in somatic cells of Drosophila. Scientific Reports 7:17890. Link doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-17973-z
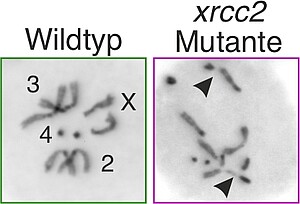
Chromosomenbrüche in DNA-Reparaturmutanten
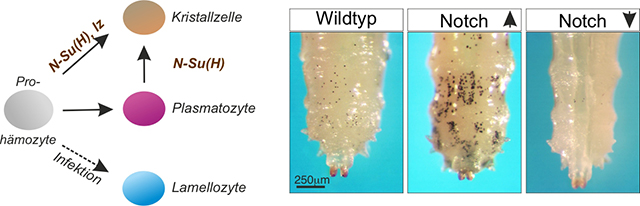
Der Notch Signalweg steuert die Zelldifferenzierung in höheren Metazoen, u.a. während der Hämatopoese (Blutbildung). Zentraler Schalter der Signalübertragung ist CSL/Su(H), ein Transkriptionsfaktor, der die Notch-Zielgene reguliert, und damit die Notch-Aktivität in zelluläre Antworten übersetzt. Wir konnten mittels Massenspektrometrie eine in vivo Phosphorylierung in der DNA-Bindedomäne von Su(H) nachweisen, wodurch ein Angriffspunkt für die Steuerung der Signalwegaktivität gegeben ist.
Weiterführende Analysen in Drosophila, in denen das native Gen durch phospho-spezifische Varianten ausgetauscht wurde, weisen auf eine spezifische Einflussnahme dieses Mechanismus in der Notch-vermittelten Blutbildung hin. Die zugrundeliegenden Prozesse werden derzeit entschlüsselt. Da die Hämatopoese auch im Säuger durch den Notch-Signalweg reguliert wird, und die Phosphorylierungsstelle in CSL hoch konserviert ist, ist eine entsprechende Regulation sehr wahrscheinlich. Vielleicht ergeben sich aus dieser Forschung neuartige Ansätze zur Leukämiebehandlung.
Dieses Projekt wird von der DFG gefördert (NA 427/5-1).
Einige projektrelevante Publikationen dazu:
Frankenreiter, L., Gahr, B.M., Schmid, H., Zimmermann, M., Deichsel, S., Hoffmeister, P., Turkiewicz, A., Borggrefe, T., Oswald, F., Nagel, A.C. (2021). Phospho-site mutations in transcription factor Suppressor of Hairless impact Notch signaling activity during hematopoiesis in Drosophila. Front. Cell Dev Biol. 9:658820. Link. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.658820
Gahr, B.M., Brändle, F., Zimmermann, M., Nagel, A.C. (2019). An RBPJ-Drosophila model reveals dependence of RBPJ protein stability on the formation of transcription-regulator complexes. Cells 8(10):1252. Link doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101252
Nagel, A.C., Auer, J.S., Schulz, A., Pfannstiel, J., Yuan, Z., Collins, C.E., Kovall, R.A., Preiss, A. (2017). Phosphorylation of Suppressor of Hairless impedes its DNA-binding activity. Scientific Reports 7(1):11820. Link doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-11952-0
| 2024 | ||
Deichsel, S., Frankenreiter, L., Fechner, J., Gahr, B.M., Zimmermann, M., Mastel, H., Preis, I., Preiss, A., Nagel, A.C. (2024): Inhibition of the Notch signal transducer CSL by Pkc53E-mediated phosphorylation to fend off parasitic immune challenge in Drosophila. eLife 2024, Nov 6;12:RP89582. doi: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.89582.3 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
Mönch, T.C., Smylla, T.K., Brändle, F., Preiss, A. and Nagel, A.C. (2024): Novel Genome-Engineered H Alleles Differentially Affect Lateral Inhibition and Cell Dichotomy Processes during Bristle Organ Development. Genes 15, 552. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/genes15050552 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
Deichsel, S., Gahr, B.M., Mastel, H., Preiss, A. and Nagel, A.C. (2024): Numerous Serine/Threonine Kinases Affect Blood Cell Homeostasis in Drosophila melanogaster. Cells 13(7):576. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13070576 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| 2023 | ||
Deichsel, S., Frankenreiter, L., Fechner, J., Gahr, B.M., Zimmermann, M., Mastel, H., Preis, I., Preiss, A., Nagel, A.C. (2023). Inhibition of Notch activity by phosphorylation of CSL in response to parasitization in Drosophila. eLife reviewed preprint: https//doi.org/10.7554/eLife.89582.1 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
Maier, D., Bauer, M., Boger, M., Sanchez Jimenez, A., Yuan, Z., Fechner, J., Scharpf, J., Kovall, R.A., Preiss, A., Nagel, A.C. (2023). Genetic and molecular interaction between H△CT, a novel allele of the Notch antagonist Hairless, and the histone chaperone Asf1 in Drosophila melanogaster. Genes 14 (1), 205. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/genes14010205 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| 2022 | ||
| Johannes Fechner, Manuela Ketelhut, Dieter Maier, Anette Preiss and Nagel, A.C., (2022). The Binding of CSL Proteins to Either Co-Activators or Co-Repressors Protects from Proteasomal Degradation Induced by MAPK-Dependent Phosphorylation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences (23):12336. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms232012336 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| 2021 | ||
Nagel, A.C., Müller, D., Zimmermann, M., Preiss, A. (2021). The membrane-bound Notch regulator Mnr supports Notch cleavage and signaling activity in Drosophila melanogaster. Biomolecules Nov 10;11(11):1672. doi: doi.org/10.3390/biom11111672https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11111672 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
Frankenreiter, L., Gahr, B.M., Schmid, H., Zimmermann, M., Deichsel, S., Hoffmeister, P., Turkiewicz, A., Borggrefe, T., Oswald, F., Nagel, A.C. (2021). Phospho-site mutations in transcription factor Suppressor of Hairless impact Notch signaling activity during hematopoiesis in Drosophila. Front. Cell Dev Biol. 14 April 2021. doi: doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.658820 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
Wolf, D.B., Maier, D., Nagel, A.C. (2021). Nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttling of murine RBPJ by Hairless protein matches that of Su(H) protein in the model system Drosophila melanogaster. Hereditas 158(1):11. doi: doi.org/10.1186/s41065-021-00175-z | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| 2020 | ||
Nagel, A.C., Maier, D., Scharpf, J., Ketelhut, M., Preiss, A. (2020). Limited availability of general co-repressors uncovered in an overexpression context during wing venation in Drosophila melanogaster. Genes (Basel) 11(10):1141. doi: doi.org/10.3390/genes11101141 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
Bayer, F.E., Deichsel, S., Mahl, P., Nagel, A.C. (2020). Drosophila xrcc2 regulates double-strand repair in somatic cells. DNA Repair (Amst.) 88:102807. doi: doi.org/10.1016/j.dnarep.2020.102807 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| 2019 | ||
Gahr, B.M., Brändle, F., Zimmermann, M., Nagel, A.C. (2019). An RBPJ-Drosophila model reveals dependence of RBPJ protein stability on the formation of transcription-regulator complexes. Cells 8(10):1252. doi: doi.org/10.3390/cells8101252 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| Wolf, D., Smylla, T.K., Reichmuth, J., Hoffmeister, P., Kober, L., Zimmermann, M., Turkiewicz, A., Borggrefe, T., Nagel, A.C., Oswald, F., Preiss, A., Maier, D. (2019). Nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttling of Drosophila Hairless/Su(H) heterodimer as a means of regulating Notch dependent transcription. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Res. 1866(10):1520-1532. doi: doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2019.07.008 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
Kober, L., Zimmermann, M., Kurz, M., Bayer, M., Nagel, A.C. (2019). Loss of putzig in the germline impedes germ cell development by inducing cell death and new niche like microenvironments. Sci Rep. 9(1):9108. doi: doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-45655-5 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
Maier, D., Nagel, A.C., Kelp, A., Preiss, A. (2019). Protein Kinase D is dispensable for development and survival of Drosophila melanogaster. G3 (Bethesda). 9(8):2477-2487. doi: doi.org/10.1534/g3.119.400307 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| 2018 | ||
| Preiss A., Nagel A.C., Praxenthaler H., Maier D. (2018): Complex genetic interactions of novel Suppressor of Hairless alleles deficient in co-repressor binding. PLoS One. 13(3):e0193056. doi: doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0193956 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| Bayer F.E., Zimmermann M., Preiss A., Nagel A.C. (2018): Overexpression of the Drosophila ATR homologous checkpoint kinase Mei-41 induces a G2/M checkpoint in Drosophila imaginal tissue. Hereditas. 155:27-39. doi: doi.org/10.1186/s41065-018-0066-4 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| 2017 | ||
| Praxenthaler H., Nagel A.C., Schulz A., Zimmermann M., Meier M., Schmid H., Preiss A., Maier D. (2017): Hairless-binding deficient Suppressor of Hairless alleles reveal Su(H) protein levels are dependent on complex formation with Hairless. PLoS Genetics. 13(5):e1006774. doi: doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1006774 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| Nagel A.C., Auer J.S., Schulz A., Pfannstiel J., Yuan Z., Collins C.E., Kovall R.A., Preiss A. (2017): Phosphorylation of Suppressor of Hairless impedes its DNA-binding activity. Scientific Reports. 19;7(1):11820. doi: doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-11952-0 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| Bayer F.E., Zimmermann M., Fischer P., Gromoll C., Preiss A., Nagel A.C. (2017): p53 and cyclin G cooperate in mediating genome stability in somatic cells of Drosophila. Scientific Reports. 7:17890. doi: doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-17973-z | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| 2016 | ||
| Nagel A.C., Szawinski J., Zimmermann M., Preiss A. (2016): Drosophila Cyclin G is a regulator of the Notch signalling pathway during wing development. PLoS One. 11(3): e0151477. doi: doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0151477 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| Fischer P., Preiss A., Nagel A.C. (2016): A triangular connection between Cyclin G, PP2A and Akt1 in the regulation of growth and metabolism in Drosophila. Fly (Austin). 10:1,11-18. doi: doi.org/10.1080/19336934.2016.1162362 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| 2015 | ||
| Auer J.S., Nagel A.C., Schulz A., Wahl V., Preiss A. (2015): MAPK-dependent phosphorylation modulates the activity of Suppressor of Hairless in Drosophil. Cellular Signalling. 27:115-124. doi: doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.10.007 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| Vicidomini R., Di Giovanni A., Petrizzo A., Iannucci L.F., Benvenuto G., Nagel A.C., Preiss A., Furia M. (2015): Loss of Drosophila pseudouridine synthase triggers apoptosis-induced proliferation and promotes cell-nonautonomous EMT. Cell Death Disease. 6(3):e1705. doi: doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2015.68 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| Zimmermann M., Kugler S.J., Schulz A., Nagel A. C. (2015): Loss of putzig activity results in apoptosis during wing imaginal development in Drosophila. in: PLOS One. 10(4):e0124652. doi: doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0124652 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| Fischer P., La Rosa M.K., Schulz A., Preiss A., Nagel A.C. (2015): Cyclin G functions as a positive regulator of growth and metabolism in Drosophila. PLOS Genetics. 11(8):e1005440. doi: doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1005440 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| Praxenthaler H., Smylla T.K., Nagel, A.C., Preiss, A., Maier D. (2015): Generation of new Hairless alleles by genomic engineering at the Hairless locus in Drosophila melanogaster. PLoS One. 10(10):e0140007. doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0140007 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| Auer J.S., Nagel A.C., Schulz A., Wahl V., Preiss A. (2015): Local overexpression of Su(H)-MAPK variants affects Notch target gene expression and adult phenotypes in Drosophila. Data in Brief. 5:852-863. doi: doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2015.11.004 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| 2014 | ||
| Nagel, A. C., Preiss, A. (2014): Mutation of potential MAPK phosphorylation sites in the Notch antagonist Hairless. Hereditas. 151:102-108. doi: doi.org/10.1111/hrd2.00066 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| 2012 | ||
| Nagel, A.C, Fischer, P., Szawinski, J., La Rosa, M.K., Preiss, A. (2012): Cyclin G is involved in meiotic recombination repair in Drosophila melanogaster. Journal of Cell Science. 125:5555-5563. doi: doi.org/10.1242/jcs.113902 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| Nagel, A. C., Szawinski, J., Fischer, P., Maier, D., Wech, I., Preiss, A. (2012): Dorso-ventral axis formation of the Drosophila oocyte requires Cyclin G. Hereditas. 149(5):186-196. doi: doi.org/10.1111/j.1601-5223.2012.02273.x | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| Volders, K., Scholz, S., Slabbaert, J.R., Nagel, A.C., Verstreken, P., Creemers, J.W., Callaerts, P., Schwärzel, M. (2012): Drosophila Rugose is a functional homolog of mammalian Neurobeachin and affects synaptic architecture, brain morphology and associative learning. Journal of Neuroscience. 32(43):15193-15204. doi: doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6424-11.2012 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| 2011 | ||
| Kugler, S.J., Gehring E.M., Wallkamm V., Krüger V., Nagel A.C. (2011): The Putzig-NURF Nucleosome Remodeling Complex is required for Ecdysone Receptor Signaling and Innate Immunity in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 188:127-139. doi: doi.org/10.1534/genetics.111.127795 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| Barisic S., Nagel A., Franz-Wachtel M., Macek B., Preiss A., Link G., Maier D., Hausser A. (2011): Phosphorylation of serine 402 impedes slingshot 1 (SSH1) phosphatase activity. EMBO Reports. 12:527-533. doi: doi.org/10.1038/embor.2011.53 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| Nagel, A.C., Preiss, A. (2011): Fine tuning of Notch signaling by differential co- repressor recruitment during eye development of Drosophila. Hereditas. 148:77-84. doi: doi.org/10.1111/j.1601-5223.2011.02221.x | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| 2010 | ||
| Kugler, S.J. and Nagel, A.C. (2010): A novel Pzg-NURF complex regulates Notch target gene activity. Molecular Biology of the Cell. Vol.21(19):3443-3448. doi: doi.org/10.1091/mbc.e10-03-0212 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| Nagel, A.C., Schmid, J., Auer, J.S., Preiss, A. and Maier, D. (2010): Constitutively active Protein kinase D acts as negative regulator of the Slingshot-phosphatase in Drosophila. Hereditas. 147(5):237-242. doi: doi.org/10.1111/j.1601-5223.2010.02200.x | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| 2009 | ||
| Protzer, C., Preiss A., Nagel A. C. (2009): Drosophila alpha-1, 4-glycosyltransferase alpha- 4GT1 inhibits reaper-mediated apoptosis in the eye. Cell and Tissue Research. 336:137-147. doi: doi.org/10.1007/s00441-009-0758-1 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| 2008 | ||
| Salvaing, J., Nagel, A. C., Mouchel-Vielh, E., Bloyer, S., Maier, D., Preiss, A. and Peronnet, F. (2008): The Enhancer of Trithorax and Polycomb Corto interacts with Cyclin G in Drosophila. PLOS One. 3(2):e1658. doi: doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0001658 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| Protzer, C. E., Wech, I. and Nagel, A. C. (2008): Hairless induces cell death by downregulation of EGFR signalling activity. Journal of Cell Science. 121(19):3167-3176. doi: doi.org/10.1242/jcs.035014 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| Daniel Paz-Gómez, Víctor Manuel Baizabal-Aguirre, Juan José Valdez-Alarcón, Marcos Cajero-Juárez, Anja C. Nagel, Anette Preiss, Dieter Maier, and Alejandro Bravo-Patiño (2008): Structural analysis of point mutations in the Hairless gene and their association with the activity of the Hairless protein. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 43(5):426-432. doi: doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2008.08.012 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| 2007 | ||
| Maier, D., Nagel, A. C., Gloc, H., Hausser, A., Kugler, S. J., Wech, I., Pfizenmaier, K. and Preiss, A. (2007): Protein Kinase D regulates several aspects of development in Drosophila melanogaster. BMC Developmental Biology. 7:74. doi: doi.org/10.1186/1471-213X-7-74 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| Kugler, S. J. and Nagel, A. C. (2007): putzig (pzg) is required for cell proliferation and regulates Notch activity in Drosophila. Molecular Biology of the Cell. 18(10):3733-40. doi: doi.org/10.1091/mbc.e07-03-0263 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| Nagel, A. C., Wech, I., Schwinkendorf, D. and Preiss, A. (2007): Involvement of co-repressors Groucho and CtBP in the regulation of single-minded in Drosophila. Hereditas. 144(5):195-205. doi: doi.org/10.1111/j.2007.0018-0661.02020.x | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| 2006 | ||
| Maier, D., Hausser, A., Nagel, A. C., Link, G., Kugler, S. J., Wech, I., Pfizenmaier, K. and Preiss, A. (2006): Drosophila protein kinase D is broadly expressed and a fraction localizes to the Golgi compartment. Gene Expr. Patterns. 6:849-856. doi: doi.org/10.1016/j.modgep.2006.03.007 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| Müller, D., Nagel, A. C., Maier, D. and Preiss, A. (2006): A molecular link between Hairless and Pros26.4, a member of the AAA-ATPase subunit of the proteasome 19S regulatory cap in Drosophila. J. Cell Sci. 2(119):250-258. doi: doi.org/10.1242/jcs.02743 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| 2005 | ||
| Müller, D., Kugler, S. J., Preiss, A., Maier, D. and Nagel., A. C. (2005): Genetic modifier screens on Hairless gain-of-function phenotypes reveal genes involved in cell differentiation and cell death. Genetics. 171:1137-1152. doi: doi.org/10.1534/genetics.105.044453 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| Nagel, A. C., Krejci, A.,Tenin, G., Bravo-Patiño, A., Bray, S., Maier, D. and Preiss, A. (2005): Hairless mediated repression of Notch target genes requires combined activity of Groucho and CtBP co-repressors. Mol. Cell Biol. 25(23):10433-10441. doi: doi.org/10.1128/mcb.25.23.10433-10441.2005 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| Wech, I. and Nagel, A. C. (2005): Mutations in rugose promote cell type specific apoptosis in the Drosophila eye. Cell Death Differ. 12(2):145-152. doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401538 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| Nagel, A. C., Maier, D. und Preiss, A. (2005): Zeit/Raum-kontrollierte RNA-Interferenz in Drosophila melanogaster. Biospektrum Sonderheft Chiptechnologie und RNA in Forschung und Anwendung. www.biospektrum.de/system/files/magazine_article/2006/03/files/86732/86732.pdf | Zeitschriftenbeitrag | |
| 2004 | ||
| Nagel, A.C., Maier, D., Krauß, S., Mezger, M. and Preiss, A. (2004): Neurogenic phenotypes induced by RNA interference with bHLH genes in the Enhancer of split complex of Drosophila melanogaster. Genesis 39. 39(2):105-114. doi: doi.org/10.1002/gene.20033 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| 2002 | ||
| Nagel, A. C., Maier, D. and Preiss, A. (2002): Green fluorescent protein as a convenient and versatile marker for studies on functional genomics in Drosophila. Genes & Evol. 212(2):93-98. doi: doi.org/10.1007/s00427-002-0210-y | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| Schreiber, S., Preiss, A., Nagel, A. C., Wech, I. and Maier, D. (2002): Genetic screen for dominant modifiers of the rough eye phenotype resulting from overexpression of the Notch antagonist Hairless in Drosophila. Genesis. 33(2):141-152. doi: doi.org/10.1002/gene.10102 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| Maier, D., Nagel, A. C. and Preiss, A. (2002): Two isoforms of the Notch antagonist Hairless are produced by differential translation initiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA. 99 (24):15480-15485. doi: doi.org/10.1073/pnas.242596699 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| 2001 | ||
| Preiss, A., Johannes, B., Nagel, A. C., Maier, D., Peters, N. and Wajant, H. G. (2001): Dynamic expression of Drosophila TRAF1 during embryogenesis and larval development. Mech. Dev. 100:109-113. doi: doi.org/10.1016/S0925-4773(00)00506-2 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| Nagel, A. C., Wech, I. and Preiss, A. (2001): scalloped and strawberry notch are target genes of Notch signaling in the context of wing margin formation. Mech. Dev. 100(1):109-113. doi: doi.org/10.1016/S0925-4773(01)00539-1 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| 2000 | ||
| Nagel, A. C., Apidianakis, Y., Wech, I., Maier, D., Delidakis, C. and Preiss, A. (2000): Neural hyperplasia induced by RNA interference with the m4/ma activity. Mech. Dev. 98:19-28. doi: doi.org/10.1016/S0925-4773(00)00446-9 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| Nagel, A. C., Maier, D. and Preiss, A. (2000): Su(H) independent activity of Hairless during mechano-sensory organ formation in Drosophila. Mech. Dev. 94:3-12. doi: | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| 1999 | ||
| Apidianakis, Y., Nagel, A. C., Chalkiadaki, A., Preiss, A. and Delidakis, C. (1999): Overexpression of the m4 and ma genes of the E(spl)-Complex antagonizes Notch mediated lateral inhibition. Mech. Dev. 86:39-50. doi: doi.org/10.1016/S0925-4773(99)00099-4 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| Maier, D., Nagel, A. C., Johannes, B. and Preiss, A. (1999): Subcellular localization of Hairless protein shows a major focus of activity within the nucleus. Mech. Dev. 89:195-199. doi: doi.org/10.1016/S0925-4773(99)00208-7 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| Nagel, A. C. and Preiss, A. (1999): Notchspl is deficient for inductive processes in the eye, and E(spl)D enhances it by interfering with proneural activity. Developmental Biology. 208:406-415. doi: doi.org/10.1006/dbio.1999.9203 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) | |
| Nagel, A. C., Yu, Y. and Preiss, A. (1999): Enhancer of split [E(spl)D] is a Gro independent, hypermorphic mutation in Drosophila. Dev. Genetics. 25:168-179. doi: doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1520-6408(1999)25:2%3C168::AID-DVG11%3E3.0.CO;2-0 | Zeitschriftenbeitrag (peer-reviewed) |

